Dr. Aso Garmyani, PhD, Stockholm Sweden
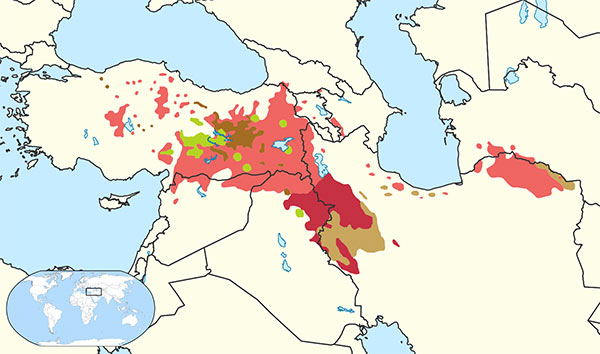
The Kurdish language is the language that the Kurdish nation has lived and spoken on a territory since ancient times. The region called Kurdistan. In other parts of the country, Kurds live and speak Kurdish.
This place (Kurdistan) human remains, sculptures, bones and skeletons of the Stone Age period have been found.
The sculptures and skeletons in the caves of Shanader and Charmo in Iraqi Kurdistan belonged to ancient people who made Kurdistan their homeland more than 60,000 years ago.
In the Kurdish Information Forum magazine, Volume 1, Part 1, 1973, Baghdad, page 591, Taha Baqir mentions that Kurdistan was prosperous sixty thousand years ago. Obviously, his people had a language and spoke it. The same language that was Kurdish still exists. However, it has been subjected to many kinds of destruction, elimination, erasure and disasters in the past and today.
Despite all the opposition of the opposition parties and all the attempts that have been made to dissolve the Kurdish language, fortunately today the Kurdish language has entered a new stage in the struggle for progress. Through written language, its dialects move towards convergence, merger, unity and progress.
The languages spoken by all the nations of the world today are divided according to the relationship of some of them to each other, in terms of grammar, phonetics and words, and each part goes back to a root.
Scientists, experts and linguists have divided these languages into several categories. Each section has given rise to the languages of several nations today, and each group is scattered.
One of these parts is called the Aryan or Indo-Iranian language family, which belongs to the Indo-European language family: Afghan, Kurdish, Persian, Tajik, Ossetian, Tati, Talshi, Avestan, Sugdi, Median, Persian or Old Persian They hold themselves. This includes some of the languages that are extinct and dead and are not used today.
The Aryan, or Indo-Iranian, language family is also divided into two categories:
- Indian Language Group
2- Iranian language group. This group is divided into three categories according to ancient, medieval and modern times:
1- Ancient languages: Median, Avestan, Old Persian.
The language of the Aryan tribes inhabiting Greater Khorasan. They took power in 250 BC, established a government and conquered all the princely states
Hold Hachameneshina
2- Medieval languages: Parthian, Fahlavi.
3- Modern Language: Kurdish, Persian.
Because linguists differ in their views on the division of Kurdish dialects, they have divided the dialects into different groups.
Kurdish belongs to the Western Iranian language group. This group is divided into two parts:
1- Northwest Iranian language group.
2- Southwest Iranian Language Group.
Kurdish belongs to the northwestern Iranian language group, but Persian belongs to the southwestern Iranian language group.
resources
1- Dr. Abdulaziz Faily. Faily. 1946. Baghdad.
2: Hadi Hafez Qaitouli. Nidaa al-Kurd newspaper. in Arabic.
Sulaimani. 2001
3- Nuri Ali Ahmad Salih. Professor Hussein Ahmad Bajalani. Faily. London. 1999.