MD Professor, Academician 0f French Academy of Sciences, Dr. Arman. Lawson. Cardiologist, PhD in Medicine, D. Sc in Neurosciences. Pavlov Institute Physiology, Russian Academy Sciences, Saint-Petersburg, Russia.
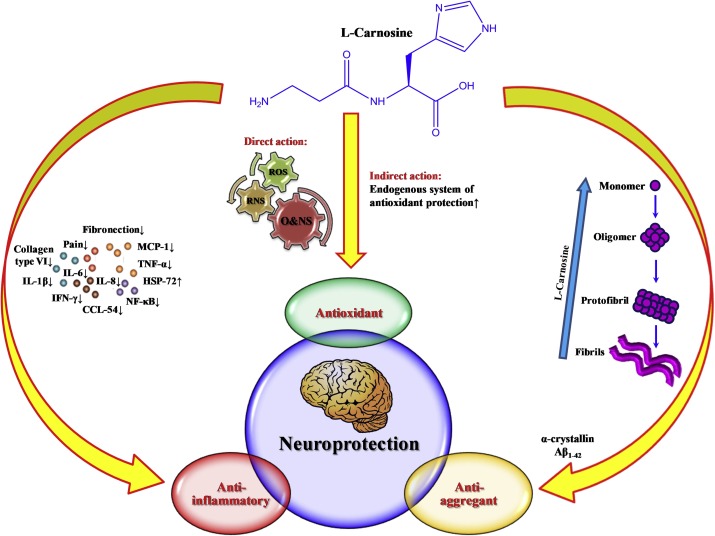
Neuroprotective properties of L-carnosine have been studied in our in vitro model on olfactory cortex slices of hypertensive rats under a long autoblood influence. Application of L-carnosine (5 mg/ml) on slice before autoblood influence leads to restoration of the activity of glutamatergic and GABA-ergic receptors inhibited by autoblood and interferes with swelling of slices. L-carnosine protects a bioelectric activity of nervous cells in case of long influence of autoblood and also renders an anti edema effect. This model of hemorrhagic stroke may provide a perspective for investigating the mechanisms of neuroprotection.
Key words: surviving brain slices, edema, focal potentials, L- carnosine.